Short Commentary
Volume 3, Issue 6
Dentogenic Blockages of the Glymphatic System and the Resulting Brain Problems
Doepp Manfred*
Head of Holistic Center, Abtwil 9030, Switzerland.
Corresponding Author :
Doepp Manfred
Email: holisticcenter1@yahoo.dec
Received : May 03, 2024 Accepted : Jun 03, 2024 Published : Jun 10, 2024 Archived : www.meddiscoveries.org
Citation: Manfred D. Dentogenic Blockages of the Glymphatic System and the Resulting Brain Problems. Med Discoveries. 2024; 3(6): 1164.
Copyright: © 2024 Manfred D. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
The brain has a glymphatic system for detoxification, which drains the toxins into the lymphatic system of the head. This system is stressed by toxin-producing processes in the mouth area to the point of blockage. A large number of toxins and foci in the mouth area are capable of doing this. The most important are osteolyses in the jawbone (NICO, FDOK). If these are not recognized and eliminated, various diseases of the brain can occur.
Our brain
At present, we are experiencing increasingly frequent brain problems.
These also have to do with coagulation disorders and reduced blood flow caused by Covid-19 viruses and their spike proteins. What is usually neglected are the problems caused by toxins in the mouth area and the resulting problems with the lymphatic drainage of the head in the context of stress on the glymphatic system.
The glymphatic system
It is a disposal system for waste products in the central nervous system of vertebrates, i.e. in the brain and spinal cord.
The name is a neologism of the terms glia and lymphatic system and was introduced by a research group led by Maiken Nedergaard (Rochester and Copenhagen).
Similar to the lymphatic system, which ends outside the meninges and does not occur in the CNS, the glymphatic system acts as a flowing circulation system for the removal of metabolic end products and toxins.
Orally
The oral system should be free of toxins so that the lymphatic system is not stressed by dentogenic toxins and the glymphatic system is not overloaded or even blocked
As a result of an overload, CNS toxins can no longer be adequately removed and accumulate in the brain. This problem and this know-how are largely unknown. Dentists and doctors (e.g. neurologists) hardly work together in this regard.
Oral Toxins, which are Important? A) Metals, i.e. heavy metals in amalgam (mercury, silver etc) and dental gold (palladium, platinum etc); light metals in implants (titanium etc). They are all toxic.
If both types of metals exist, a production of electric current takes place (dental galvanic voltage). This may be 1,000 times higher than the physiological voltages which are used by the brain.
In case of a perforated blood-brain-barrier (by means of electro-smog) the metals can penetrate into the brain and accumulate in the glands of the brain.
Oral Toxins, which are Important? B) Chronic bacterial inflammation of the gingiva and/or gums, especially hidden gangrenous stomatitis/pulp, pulpitis, and periapical granuloma findings.
The starting point is often inadequate root canal treatment, in which dead tissue and germs remain in the root canals. According to experts, around 80% of these treatments are insufficient.
Periapical granuloma, also sometimes referred to as a radicular granuloma or apical granuloma, is an inflammation at the tip of a dead (nonvital) tooth, resulting in inflammation of granulation tissue at the root tips of a dead tooth.
Oral Toxins, which are Important? C) Jaw bone foci in the sense of non-infectious chronic ostititis: NICO, FDOK. Also: fatty degenerative jaw osteitis.
Chronic softening of the jawbone is a phenomenon that is still not recognized by many areas of medicine and dentistry, or at least its health effects are not taken seriously. These “jaw inflammations” were described by the American pathologist Professor Bouquot as “Neuralgia Inducing Cavitational Osteonecrosis” (NICO).
NICO is a deficiency in the form of a metabolic disorder that leads to fatty degenerative bone dissolution. NICO usually presents as fatty lumps that are easily spooned out of the medullary canal of the jawbone. These degenerated fat cells in NICO areas produce inflammatory messengers (cytokines/chemokines like RANTES) that affect other organs where they can be associated with breast cancer, Hashimoto’s, multiple sclerosis, etc.
Oral Toxins, which are Important? D) Periodontitis and gum pockets filled with problematic pathoogens.
The tooth is anchored in the tooth socket by gomphosis, i.e. a tooth is only suspended in its bone socket via the Sharpey fibers and is not firmly fused to it. There is therefore a natural gap (= periodontal gap) between the tooth and the bone, in which the Sharpey fibers and periodontal ligament are located.
Bacteria can penetrate this gap. Especially those that feel very comfortable in this environment (= obligate anaerobes) multiply and lead to inflammation in which the Sharpey fibers are damaged. The periodontium recedes and inflammatory niches, known as periodontal pockets, develop in the periodontal gap, which can repeatedly and acutely fill with pus.
Rantes
CCL5 (CC chemokine ligand 5) is a cytokine from the CC chemokine family.
CCL5 is involved in inflammatory processes. CCL5 is formed, among other things, by cytotoxic T cells and binds T cells, monocytes and eosinophils by binding the receptors CCR3, [1,2] CCR5 [2-4] and CCR1 [2,4]. CCL5 activates the GPCR GPR75 [5].
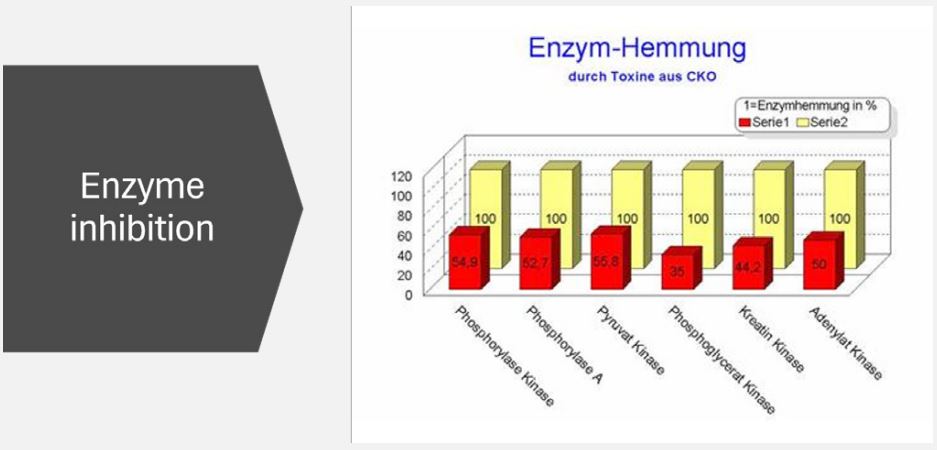
Enzyme inhibition by toxins from the NICO area
How do toxins develop? Toxins are produced by bacterial colonization in the jawbone and are increasingly found in the NICO area. These toxins cannot be visualized by X-ray. What effects do the toxins have? The toxins can lead to a significant inhibition of vital enzymes in the cell and thus to mitochondriopathy, which is now considered by many researchers to be a key factor in the development of cancer.
This makes the foci in the jawbone important for chronic diseases - although X-rays do not allow a reliable diagnosis to be made. This leads to the holistic conclusion that even if no dead/root-filled teeth are present, systemic sensitization of the immune system by mercaptans/thioethers from NICO areas should be investigated.
Effects (1)
As a result of those disorders, the brain cannot detoxify itself sufficiently and accumulates toxins. Different brain diseases can be triggered depending on the individual`s previous exposure.
In the preliminary stages, there is the phenomenon of «brain fog» with symptoms such as dizziness, concentration problems and fatigue. Later dementia or Alzheimer`s follow.
Effects (2)
After intensive dental diagnostics with digital computer tomography and ultrasound (CaviTAU), we have regularly found dentogenic and jaw findings, and improvements in symptoms after treatment.
The usual X-ray is insufficient
These examinations should be carried out in all cases where there are unclear brain-related problems.
However- as mentioned - also severe diseases far from the brain (like breast cancer) can be connected and react positively on the removal of the dental focus.
Conclusion
The brain has a glymphatic system for detoxification, which drains the toxins into the lymphatic system of the head.
This system is stressed by toxin-producing processes in the mouth area to the point of blockage. A large number of toxins and foci in the mouth area are capable of doing this.
The most important are osteolyses in the jawbone (NICO, FDOK). If these are not recognized and eliminated, various diseases of the brain can occur.
References
- Doepp Manfred. Topic: Mouth, Teeth, and Dentition; Journal of Advances in Bioengineering and Biomedical Science Research (ISSN: 2640-4133); 5(3): 186-187. doi.org/10.33140/ABBSR.05.03.04
- Doepp Manfred. Significant Findings in Tooth Roots and Jaw Bones Can Cause Serious Diseases. Clinical Research and Clinical Trials. 2022; 6(1). DOI: 10.31579/2693-4779/100
- Doepp Manfred, Could Dentistry Be a Major Factor in Human Poisonings? IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences, (IOSR-JDMS). 20022; 21(03): 48-49. ISSN: 2279-0853, DOI: 10.9790/0853-2103104849.
- Doepp Manfred. Our Brains are Targets No. 1, Cleared for Firing - an Overview. American Journal of Biomedical Science & Research. 2021; 14(3). AJBSR. MS.ID.001986. DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2021.14.001986.
- Lechner J. Herd, Regulation und Information - Störfelder im Zahn, Mund- und Kieferbereich; HÜTHIG Verlag Heidelberg, 1. Auflage.1993.
- Lechner J. Störfelder im Trigeminusbereich und Systemerkrankungen: Ein systemisches Sanierungskonzept für Zahn-Störfelder, Verlag für Ganzheitliche Medizin. 1999.
- Bouquot JE, Roberts AM, Person P, Christian J. NICO (neuralgiainducing cavitational osteonecrosis): osteomyelitis in 224 jawbone samples from patients with facial neuralgia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1992; 73: 307-319.
- BOUQUOT JE, CHRISTIAN J. Long term effects of jawbone curettage on the pain of facial neuralgia. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1995; 53: 387-397.
- Bouquot JE, Roberts A. NICO (neuralgia-inducing cavitational osteonecrosis): Radiographic appearance of the invisible osteomyelitis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1992; 74: 600.
- Lechner J. NICO - Ist fehlende röntgenologische Evidenz Beweis fehlender klinischer Existenz? 2010 ZWR Nov. 2010; 578-592.
- Bouquot Je, Shankland Ii, We, Margolis M. Through transmission alveolar ultrasonography (TAU) - new technology for evaluation of bone density and desiccation. Comparison with radiology of 170 biopsied alveolar sites of osteoporotic and ischemic disease. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002; 92: 550.
- Proud foot AE, Fritchley S, Borlat F, Shaw JP, Vilbois F, et al. The BBXB motif of RANTES is the principal site for heparin binding and controls receptor selectivity. In: J. Biol. Chem. 2001; 10620-6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010867200.
- Ignatov A, Robert J, Gregory-Evans C, Schaller HC. RANTES stimulates Ca2+ mobilization and inositol trisphosphate (IP3) formation in cells transfected with G protein-coupled receptor 75. In: Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006; 490-7. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706909, PMID 17001303.
- Cocchi F, DeVico AL, Garzino-Demo A, Arya SK, Gallo RC, et al. Identification of RANTES, MIP-1 alpha, and MIP-1 beta as the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ T cells. In: Science. 270. 1995; 1811-5. doi:10.1126/science.270.5243.1811.