Clinical Image
Volume 3, Issue 3
A Case of Dysphagia due to an Esophageal Duplication Cyst in a Difficult Anatomical Site: A Challenging Situation for Endoscopic Treatment
Christos Sotiropoulos*; Christos Konstantakis; Odysseas Ampazis; Georgia Diamantopoulou, Georgios Theocharis; Christos Triantos; Konstantinos Thomopoulos
Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University General Hospital of Patras, Greece.
Corresponding Author :
Christos Sotiropoulos
Email: cr.sotiropoulos@hotmail.com
Received : Feb 20, 2024 Accepted : Mar 22, 2024 Published : Mar 29, 2024 Archived : www.meddiscoveries.org
Citation: Sotiropoulos C, Konstantakis C, Ampazis O, Diamantopoulou G, Theocharis G, et al. A Case of Dysphagia due to an Esophageal Duplication Cyst in a Difficult Anatomical Site: A Challenging Situation for Endoscopic Treatment. Med Discoveries. 2024; 3(3): 1137.
Copyright:Sotiropoulos C © 2024 . This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Introduction
Esophageal duplication cyst is a rare congenital cyst that results from aberration of the posterior division of the embryonic foregut at the fourth to eighth week of gestation. Most of these cysts become symptomatic in childhood, whereas in adults they are usually an asymptomatic incidental radiographic or endoscopic finding. They may cause symptoms due to compression, rupture and inflammation of the esophagus or the respiratory system and require intervention and treatment when being symptomatic.
Case report
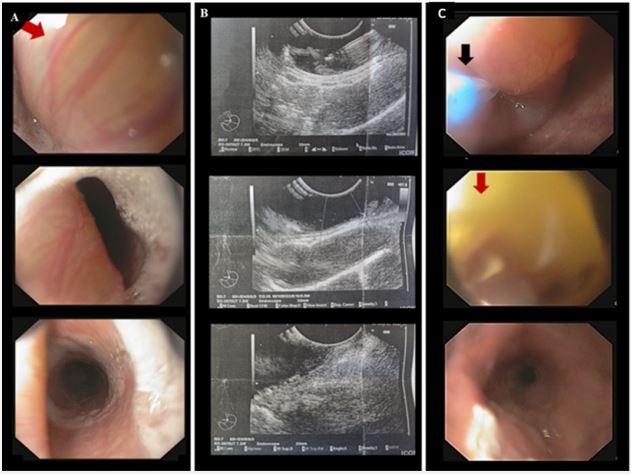
We report the case of an 83-year-old patient with a history of metabolic syndrome and heart disease who presented with a five month history of dysphagia, mainly on solid food and during the passage of food through the upper esophageal sphincter (UES). An esophagogram showed a filling deficit below the UES and esophagoscopy revealed a polypoid projecting mass (Figure 1A) immediately after the UES, with smooth mucosa causing narrowing (but not obstruction) of the lumen. The patient underwent an endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) to identify this polypoid mass which revealed characteristics of a clear submucosal formation located in the area of the 3rd ultrasound layer (Figure 1B), with preservation of the integrity and sound structure of the other layers. After aspiration of the content a thick mucous amorphous material was drained (mucous cyst) that was negative for malignancy. The patient was treated with a minimally invasive technique, re-endoscopy was performed and the cyst was opened with a longitudinal fissure with a needle-knife sphincterotomy, with subsequent outflow of copious yellow-gray mucous contents and flattening of the cyst (Figure 1C). Two months later, the patient remained asymptomatic and no cyst recurrence was observed during endoscopic follow-up.
Conclusion
Esophageal duplication cyst should be considered in the differential diagnosis in any patient presenting with gastrointestinal symptoms such as dysphagia. Treatment for this condition is currently moving from surgery to endoscopic interventions when endoscopic ultrasound demonstrates that the cysts are located within the submucosal layer and do not communicate with the deep muscle layer. Small duplication cysts can be removed completely with a polypectomy loop or with an insulated tip knife safely and effectively.
References
- Bagheri R, Asnaashari AM, Afghani R. Esophageal duplication cyst. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2015; 23(3): 332-4.
- Kolomainen D, Hurley PR, Ebbs SR. Esophageal duplication cyst: case report and review of the literature. Dis Esophagus. 1998; 11(1): 62-5.
- Nishikawa J, Nagao M, Ogawa R, Sasaki S, Goto A, Okamoto T, Sakaida I. Endoscopic treatment of an esophageal duplication cyst. Endoscopy. 2017; 49(S 01): E107-E108.
- Wiechowska-Kozłowska A, Wunsch E, Majewski M, Milkiewicz P. Esophageal duplication cysts: endosonographic findings in asymptomatic patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18(11): 1270-2.