Opinion Article
Volume 2, Issue 2
Aspirin, the Feasibility as a Binding Inhibitor
Toshihiko Hanai*
Health Research Foundation, Research Institute for Production Development 4F, Sakyo-Ku, Kyoto, Japan.
Corresponding Author :
Toshihiko Hanai
Tel: 81-45-295-1468
Email: hanai104@kf7.so-net.ne.jp
Received : Jan 18, 2023 Accepted : Feb 24, 2023 Published : Mar 03, 2023 Archived : www.meddiscoveries.org
Citation: Hanai T. Aspirin, the Feasibility as a Binding Inhibitor. Med Discoveries. 2023; 2(2): 1019.
Copyright: © 2023 Hanai T. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Introduction
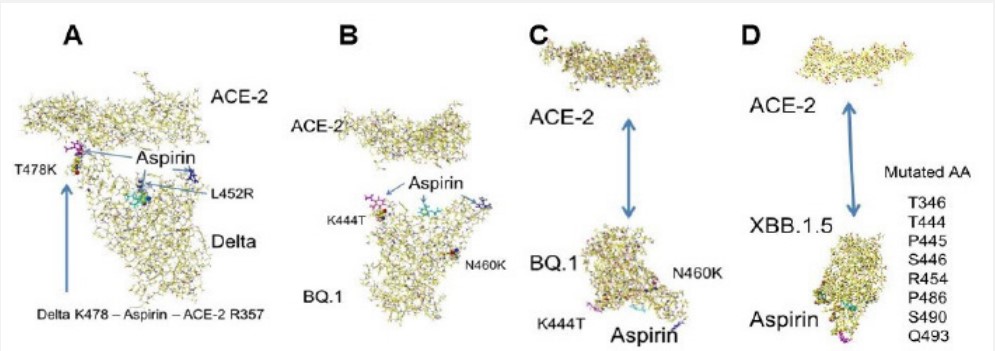
Aspirin is a popular flu medicine and trying to use in curing Covid-19 patients; however, the effectiveness was mixed results, and the variant types were not provided in the reports [1-3]. In silico analysis demonstrated that it did not inhibit the binding of Delta S-RBD with ACE-2. Rather, it bridges the binding of Delta S-RBD K478 with ACE-2 R317 (Figure 1A) [4]. The binding affinity of current spreading BQ.1 and XBB.1.5 (MIFS: 309.9 and 373.9 kcal mol-1, respectively) is weaker than that of the Delta variant (594.2 kcal mol-1), and they do not contain extra basic amino acids at the binding site [5]. Therefore, the feasibility of aspirin binding inhibition was studied.
Results and discussion
The initial location of three aspirin locations is shown as the molecular color in Figure 1B, as demonstrated for other compounds [4,5]. After optimization of these complexes using an MM2 program, the aspirin-bound BQ.1 and XBB.1.5 S-RBD complexes were repulsed from ACE-2. The aspirin binding site is completely repulsed in Figures 1C and 1D due to the ion-ion repulsion. The in silico analysis of molecular interactions indicated that aspirin should also inhibit the binding like other carboxylic compounds among 170 compounds analyzed [4,5].
Conclusion
Such in silico analysis of molecular interactions should help to understand the feasibility of binding inhibitors. The actual experiment using viruses is required before studying animal tests. Overdose of medicines should be avoided, as overtaking vitamins and amino acids has caused health problems.
References
- Kim I, Yoon S, Kim M, Lee H, Park S, Kim W et al. Aspirin is Related to Worse Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021; 57(9): 931. doi: 10.3390/medicina57090931.
- Bloom J. Aspirin Reduces Ventilation and Deaths in Hospitalized. American Council on Science and Health. 2021. https://www. acsh.org/news/2021/06/15/aspirin-reduces.
- Hui A. Aspirin Didn’t Improve Survival for Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients, Study Finds. Coronavirus News. 2022. https://www. verywellhealth.com/aspirin-covid-treatment.
- Hanai T. Quantitative in silico analysis of SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD omicron mutant transmissibility, Talanta. 2022; 240: 123206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123206.
- Hanai T. Further quantitative in silico analysis of SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD Omicron BA.4, BA.5, BA.2.75, BQ.1, and BQ.1.1 transmissibility. Talanta. 2023; 241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.124127 3.